CMDB Reconciliation and Remediation
Manage & Optimize Assets
Introduction
CMDB Reconciliation is the process of comparing existing sources of Inventory Data against active devices in the network and validating that the data reported on these active devices is accurate and consistent with expectations.
Audience: CMDB Analysts, CMDB Management, Auditors
Difficulty: Intermediate to Advanced
Execution Time: 1 month (initial queries), 6 months (end-to-end Enforcements)
Duration of Use Case: Perpetual
Value: Time, cost, & risk reduction
What is this use case?
Configuration Management Database (or CMDB) Reconciliation is the process of truing up an organization's system of record for their asset data with the current footprint of their assets. Often when a CMDB is implemented, it is incomplete and contains incorrect data (such as mis-categorized and stale data). This use case seeks to correct that.
Use Case in Action:
The more adapters you have connected in Axonius, the more data you’ll receive about each asset. We recommend any of the following adapter types are configured in your environment before enabling the CMDB create/update assets enforcements.
- CMDB Platforms
- Identity Access Management
- MDM/EMM
- Configuration Patch Management
- Endpoint Protection
- Networking
- Vulnerability Assessment Tools
- Cloud and Virtualization
Why is it Relevant?
- Organizations will want to undertake this use case to meet regulatory requirements for complete asset records.
- Reduction of the time taken to identify devices missing from their CMDB.
- Lower the cost of maintaining the CMDB through automation of information updates.
Scope
How do I build this use case?
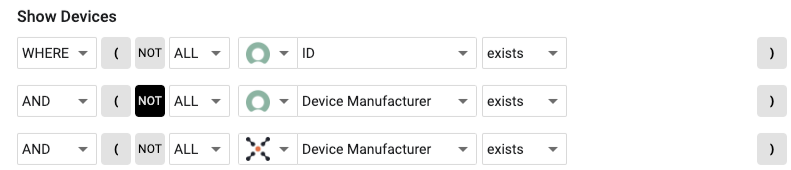
The baseline to find anything not listed in your CMDB is to use the NOT flag and select the CMDB platform adapter connected in Axonius.
-
Scoping Queries
-
Establish what assets are in-scope or out-of-scope:
-
Examples:
- OS Types
- Last Seen Days
- Adapter Properties
- NOT CMBD Exists
-
-

Reconciliation Queries
-
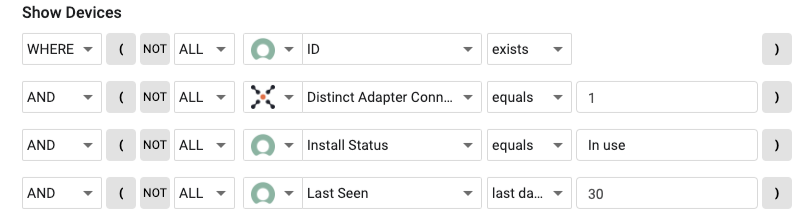
Establish what assets or fields are missing or incorrect in the CMDB.
-
Examples:
- Base Queries
- Single Adapter
- Install Status
- Fields missing from CMDB
- Missing Specific Adapters
-
Visibility
How do I visually explain this use case?
Reporting on CMDB reconciliation is often expected as a singular number: What percentage of my devices are missing or have discrepancies in our CMDB? However, visually explaining the project's scope and progress with varying data points will ensure executives and system owners understand the project's progress.
Recommended Visualizations
There are several key visualizations we recommend when starting this use case which attempt to answer key questions by leadership/executives.
Enrichment Status– How many devices are currently missing critical fields in CMDB?
Asset Creation Trend– How many assets have been created/updated with Axonius Enforcements?
Adapter Metrics – How can we identify the main source of our discrepancies?
Actionability
How do I automate this use case?
Automation is a key component for reconciling your CMDB
Reporting
Automatically deliver timely, detailed, and accurate reports to stakeholders through emails, PDF reports, and CSV exports.
Examples Include:
- Send Email
- Send CSV to S3
- Send CSV to Azure Storage
- Microsoft Teams – Send Message
- Slack – Send Message
- Reports (Send Dashboard)
Fully Automated CMDB Reconciliation
In order to further automate the CMDB Reconciliation process, additional testing and considerations should be reviewed.
1 - Review the CMDB Adapter Advanced Configuration
-
ServiceNow:
-
Use 'cmdb_ci' table instead of 'alm_asset' table for install status and location
-
Advanced fields to show in basic view (Devices, Business Applications, Databases)
- Fetch IP addresses
- Install Status/Operational Status Include list
- Do not add serial number metadata
-
Jira SM:
- Filter Device object types
2 - Important Fields
-
ServiceNow:
- Operational Status or Install Status or Asset Install Status or Hardware Status?
- Class Name, Sys ID
- Discovery Source, Updated by, Created by, Source Application
Jira SM:
- Object Key
- Object Type
3 - Select Trusted Adapters
Determine which adapters will have the most trusted data for each field
Review the Data
Analyze and normalize the fields that will be needed.
Determine Key Fields
-
Find what fields, if any, are required to be unique within their CMDB instances
- Sometimes this can be Hostname, Serial Number, or a combination
Find out what fields are required when adding a new asset of each asset class
- Different asset classes may require a minimum set of fields to be created in their CMDB. For example, Servers may require IP/MAC, Virtual Machines may require the name of their virtual host
Determine the mapping between the CMDB fields and Axonius fields
- u_ fields are usually custom fields on the CMDB side
Normalize Key Fields
-
Use Field Segmentation charts to determine all values used for each field that will be populated into the CMDB, such as OS: Type and Definition, Device Model, and Device Manufacturer
-
Will these values be normalized by the CMDB
- Do these values exist in a look-up table?
- Use values found in the Field Segmentation chart to manually populate new values
Will these values be normalized by Axonius?
- Use Custom Data EC actions
Automation Implementation
Define Reference Queries
-
Consider excluding the following:
- Systems missing key fields
- Systems with recent first fetches
- Over correlated systems
- Single-adapter devices
Identify systems that should be retired
- Based on last seen, excluding the CMDB
Define Target Queries
- Create queries for each Asset Class you will be updating
- Work to define asset classes such as Servers, Workstations, Virtualization hosts, etc.
- Check overlaps between these and Asset Classes defined within their CMDB
Select a Pilot Group
- Find an Asset Class with a majority of its devices with defined key fields
- Find an Asset Class with minimal or no overlaps with other classes
Key Design Decisions
-
Test / Prod Considerations
- Create queries to filter based on asset entity / adapter connections
- Configure the EC actions to target the correct Asset Entities
Create + Update OR Create only?
-
Using ServiceNow IRE?
- Use only a Create EC Action
- Use the correct Options in the EC actions
Not using IRE?
- Use both Create and Update
- Create Queries to target the correct devices for either Creating or Updating
- Use the correct Options in the EC actions
Retiring Assets
- Select the correct field for tracking retirement Status
- Use an update action
Automation Maintenance
-
Dashboards
- Visualize overlaps between classes, environments, and statuses
- Visualize changes in numbers of Update, Create, and Retirement targets over time
Alerts
- Create alerts for major changes in numbers
- Create alerts for the number of failed EC actions
Updated 4 months ago
