Managing Data Scopes
Use data scopes to allow users to see only data that is relevant to them or their role. A data scope is a subset of all the data in your environment. Users assigned a specific data scope can only see the data that is available to that data scope.
Data scopes are useful, for example, when there are different teams, departments, or geographic regions in an organization that each need access to specific assets. While you want one instance of Axonius to be installed for your organization, you want each team, department, or geographic region to only see information about their own assets, thereby creating a closed environment for each.
Each data scope has separate entities: queries, dashboards, Enforcement Sets and reports. When a data scope is first created, it is empty and does not include any of these entities. Access to each entity is defined by the permissions selected when creating them. They can also be moved from one permission level to another.
- See Creating Queries with the Query Wizard for more about creating queries.
- See Working with Dashboards for more about creating dashboards.
- See Creating Enforcement Sets for more about creating Enforcement Sets.
- See Configuring Reports for more about Reports.
There are two types of data scopes:
- Global Data Scope - Users assigned the global data scope have access to all assets in the environment. Any role can be assigned the global data scope. The global data scope is created by Axonius and is not defined by an asset scope query.
- All other data scopes - These are all other data scopes you create. A user assigned a data scope can only see the information contained in that data scope.
Note:
When a user is assigned to a specific data scope, the following permissions are not available:
System Management
Activity Logs
Sharing data across data scopes
When a user with User Admin permissions is assigned a data scope, that user can create and manage users within the data scope.
Resources, such as dashboards and queries, that have access permissions of Private are available only to the user who created them and only within the data scope where they were created.
Adapter Fetch History saved queries
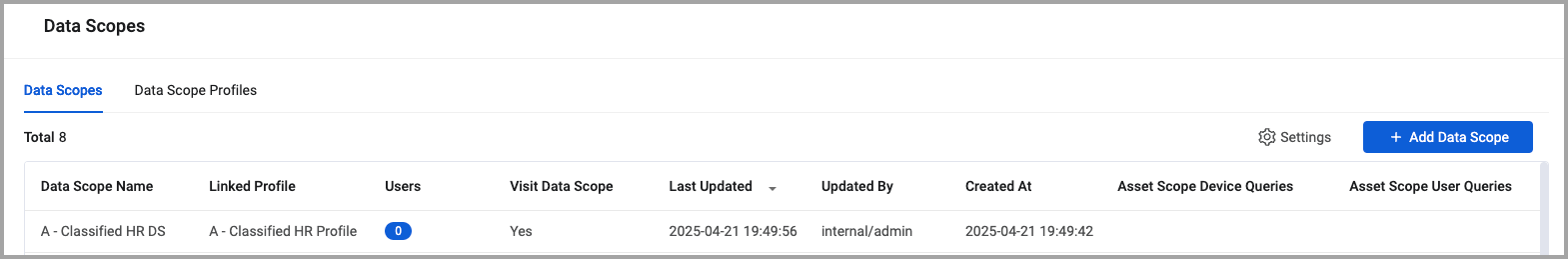
Data scopes are listed on the Data Scopes tab of the Data Scopes page.
To access the Data Scopes page:
- From the top right corner of any page, click
 . The System Settings page opens.
. The System Settings page opens. - In the Categories/Subcategories pane of the System Settings page, expand User and Role Management, and select Data Scopes.
- The Data Scopes page is displayed with the Data Scopes tab selected.
- The Data Scopes page has two tabs: Data Scopes and Data Scope Profiles. See Data Scope Profiles for more about using profiles.
The Data Scopes tab provides the following information:
- Data Scope Name - The name of the data scope.
- Users - The number of users that have access to the data scope.
- Visit Data Scope - Indicates whether users not assigned the data scope as their Main data scope can visit this data scope.
- Last Updated - The time stamp when the data scope was last updated.
- Updated By - The user that last updated the data scope.
- Created At - The time stamp indicating when the data scope was created.
- Asset Scope Device Queries - The asset scope device queries used by the data scope.
- Asset Scope User Queries - The asset scope user queries used by the data scope.
Defining a Data Scope
When adding assets to a data scope, the configuration of asset subsets is inherited from the main asset type.
To define a data scope:
- From the Data Scopes page, click + Add Data Scope.
- Define which assets are included in the data scope according to the following methods.
There are a number of ways to define what assets are available in a data scope.
- Define by Assets - You can define a data scope by selecting what asset types are to be included, Define by Assets. Then, for each asset type you can refine and further specify the included assets by creating a query that returns the assets to be included or by selecting specific fields to include or exclude from the data scope.
- You can also apply a data scope profile to use a saved configuration of included or excluded fields.
- Define by Adapter - The list of assets included in the data scope is defined by the selected adapter connections. Only those assets are included. However, the data for these assets can come from any adapter connection.
- Restrict Data - You can hide adapter connection information and restrict data within a data scope by cloud account:
- Adapter connection information - By default, information about adapter connections is visible to users who can access the data scope. You can restrict the visibility of adapter connection here. Select the adapter connections whose information you want to block within the data scope.
- Cloud Accounts - You can select which cloud accounts are visible to the data scope in the Cloud Compliance Center.
You can combine these methods to define a data scope. For example, you can include only Device assets in a data scope that are fetched by specific adapter connections.
Note:
Dashboards and queries with an access permission of Private are only available to the user who created them and only within the assigned data scope where they were created.
Defining a Data Scope by Assets
Only assets of the selected types will be available in the data scope, in combination with any selections made on the Define by Adapters tab.
To define a data scope by assets:
-
In the Define by Assets tab, search for or select the asset types to include in the data scope and click Apply. The number of selected asset types is indicated next to the tab name and a collapsible section is added below for each selected asset type, in their order of selection. An
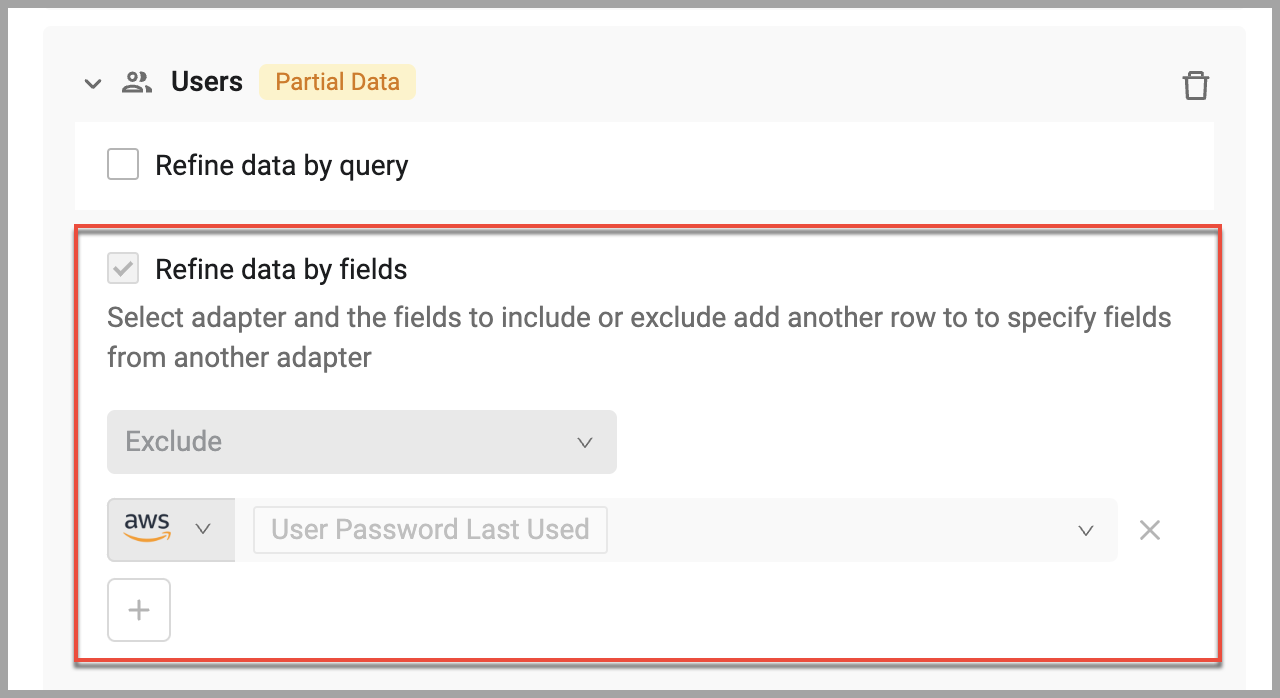
All Datatag appears next to each asset type to indicate that all assets of this type are included in the data scope.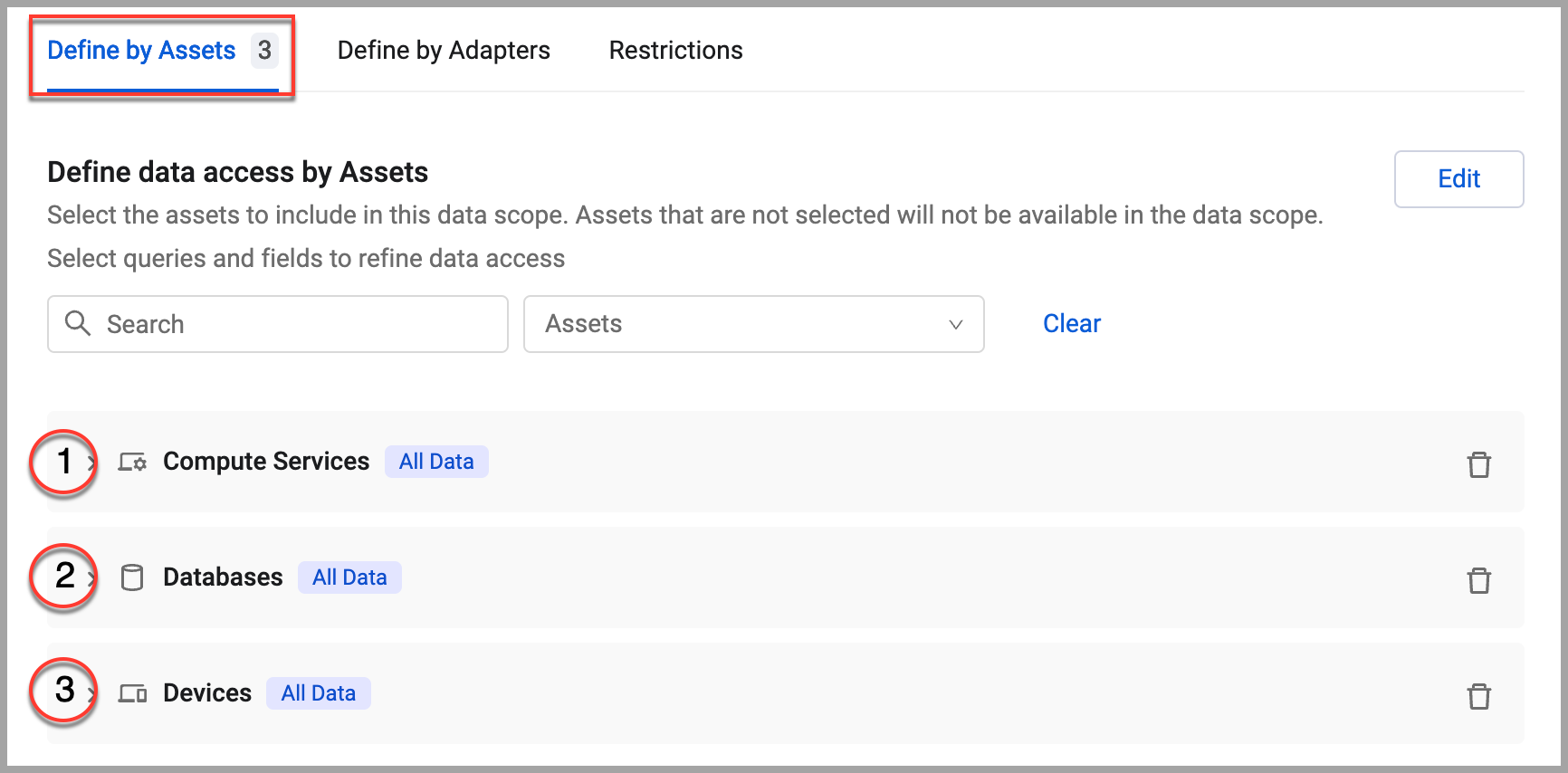
-
You can further specify what assets are included in the data scope by using a query and/or specifying that the data of specific fields be included or excluded.
- To select an asset scope query, expand the asset type and select Refine data by query. From the list, select the asset scope query that returns the assets you want included in the data scope. Click
+to add more queries. You can add as many as needed. To remove a query, click the x to the right. When an asset scope query is used, aPartial Datatag appears to indicate that only a subset of available assets of this type are included in the data scope. See Creating an Asset Scope Query.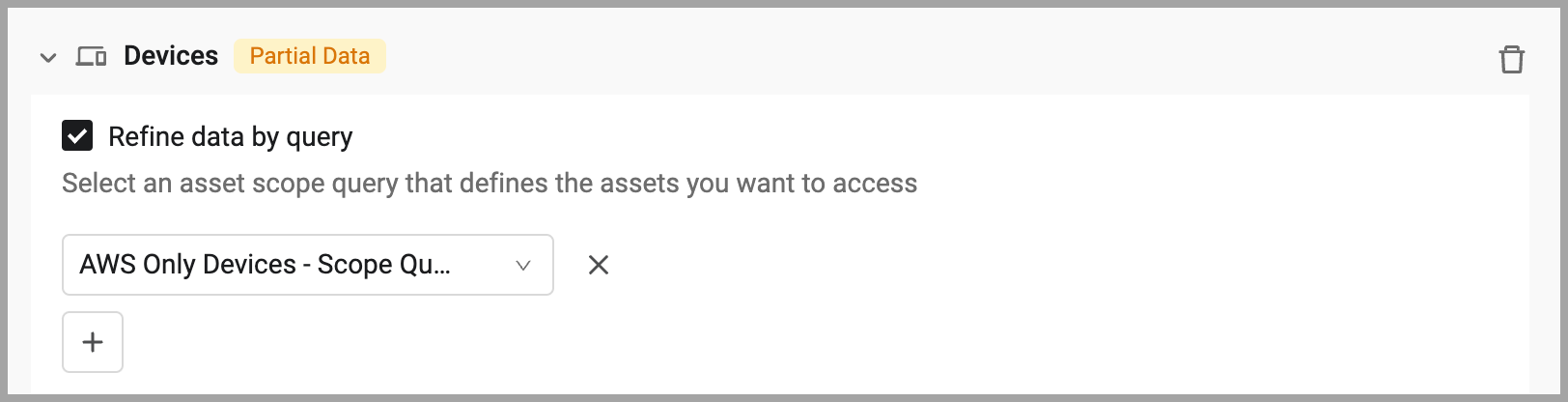
- To include/exclude fields, expand the asset type and select Refine data by fields. When fields are included or excluded, a
Partial Datatag appears to indicate that only a subset of available assets of this type are included in the data scope.
- To select an asset scope query, expand the asset type and select Refine data by query. From the list, select the asset scope query that returns the assets you want included in the data scope. Click
Using Data Scope Profiles
Instead of defining included and excluded fields for every data scope individually, you can apply a data scope profile. When a profile is applied, the Refine data by fields option is disabled and the field configurations from the profile are shown greyed.
The
Partial Datatag appears next to the asset type name.To use profiles they must be enabled for all data scopes. See Data Scope Settings. When data scope profiles are enabled, the "Data scope profile" section is added to the top of the data scope configuration drawer (including existing data scopes). There you need to enable profiles for the individual data scope. See Applying a Profile to a Data Scope.
Select either Include or Exclude.
- Include - Select all fields you want to appear in the data scope. All other field names and data are hidden.
- Exclude - Select all the fields you do not want to appear in the data scope. The field names and all field data are hidden.
Notes:
When specific fields are excluded from a data scope, the following modules will not be available to the data scope:
Data Analytics
Asset Investigation
These types of fields cannot be excluded from a data scope:
Preferred fields
Adapter-specific fields related to an aggregated field (e.g. AWS hostname)
Fields that Axonius correlation is based upon
Within Asset Profile, the XML and JSON format tabs will not be available.
The related modules of Software and Aggregated Security Findings will not be restricted even when those fields are restricted within any asset type.
- Do one of the following:
- Go to the Define by Adapters tab to further define the data scope to include assets according to the adapter connection used to fetch them. Selections in all tabs combine to define the data scope.
- Go to the Restrictions tab to manage adapter configuration information and cloud accounts.
- Click Save to create the data scope as it is currently defined combined with the selections on the Define by Assets tab.
- Assign data scopes to users to give access to specific users. Users are assigned a main data scope in the process of creation.
Defining a Data Scope by Adapter
Only assets from the selected adapters and adapter connections are included in the data scope, in combination with any selections made on the Define by Assets tab.
To define a data scope by adapter connections:
- In the Define by Adapters tab, and select Define data by adapter connections.
Notes
- The data scope will include only assets from the selected adapter connections. When specific asset types are selected on the Define by Assets tab, those selections combine with the assets in the Define by Assets tab.
- Up to 50 adapter connections when defining a data scope by adapter.
-
- Select how to specify what adapter connections are included in the data scope:
- Include only - Select the adapter connections whose assets you want included in the data scope. Only assets and asset data from these adapter connections are included in the data scope.
- Include all but - Select the adapter connections whose assets you do not want included in the data scope. All assets and data from all other adapter connections will be included in the data scope.
- Exclude - Select the adapter connection whose assets you do not want included in the data scope. All assets and data from all other adapter connections will be included in the data scope.
- Select how to specify what adapter connections are included in the data scope:
-
Click the adapters list, then select adapters and/or adapter connections.
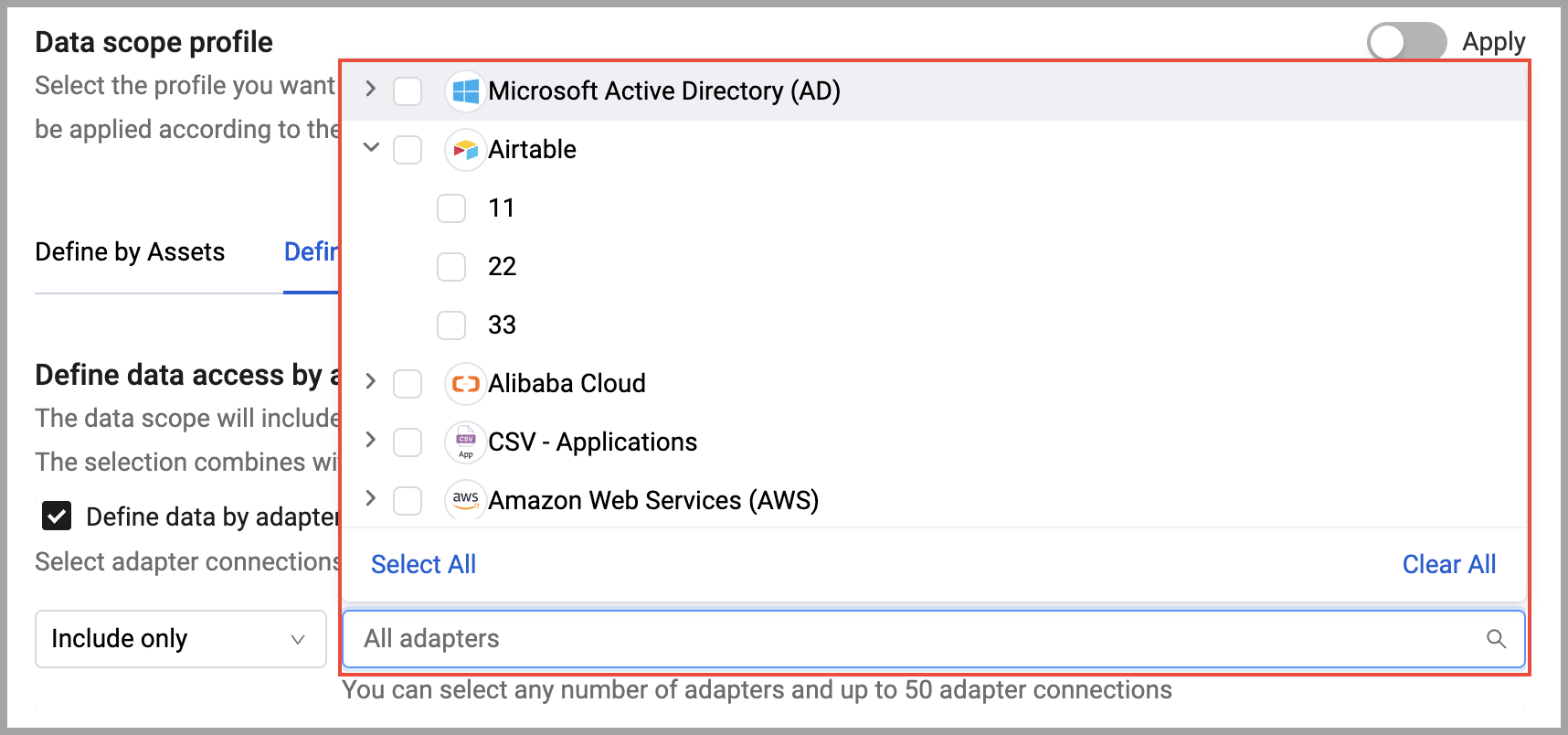
-
To hide all data from specific adapters, select Hide data by adapter and select from the list the adapters you want to NOT appear in the data scope. All data fetched via the selected adapters will not be included in the data scope. Note that some data may be fetched by more than one adapter and may appear in the data scope from that other source.
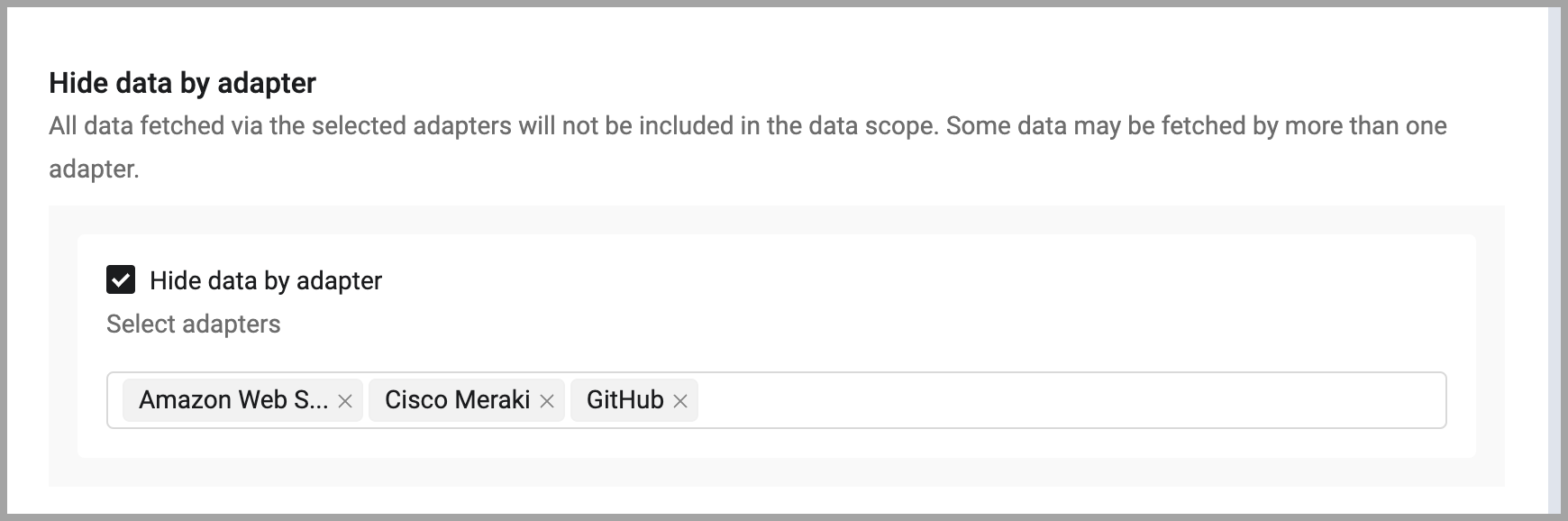
-
Optionally, do one of the following:
- Go to the Restrictions tab to manage adapter configuration information and cloud accounts.
- Go to the Define by Assets tab to select specific asset types in the data scope. Selections in all tabs combine to define the data scope.
-
Click Save to create the data scope as it is currently defined combined with the selections on the Define by Assets tab.
Managing Adapter Connection Information
You can decide to hide or review adapter connection information within a data scope. When adapter connection information is available, users can view it in the adapter profile page. When hidden, this information is not visible by users in the data scope.
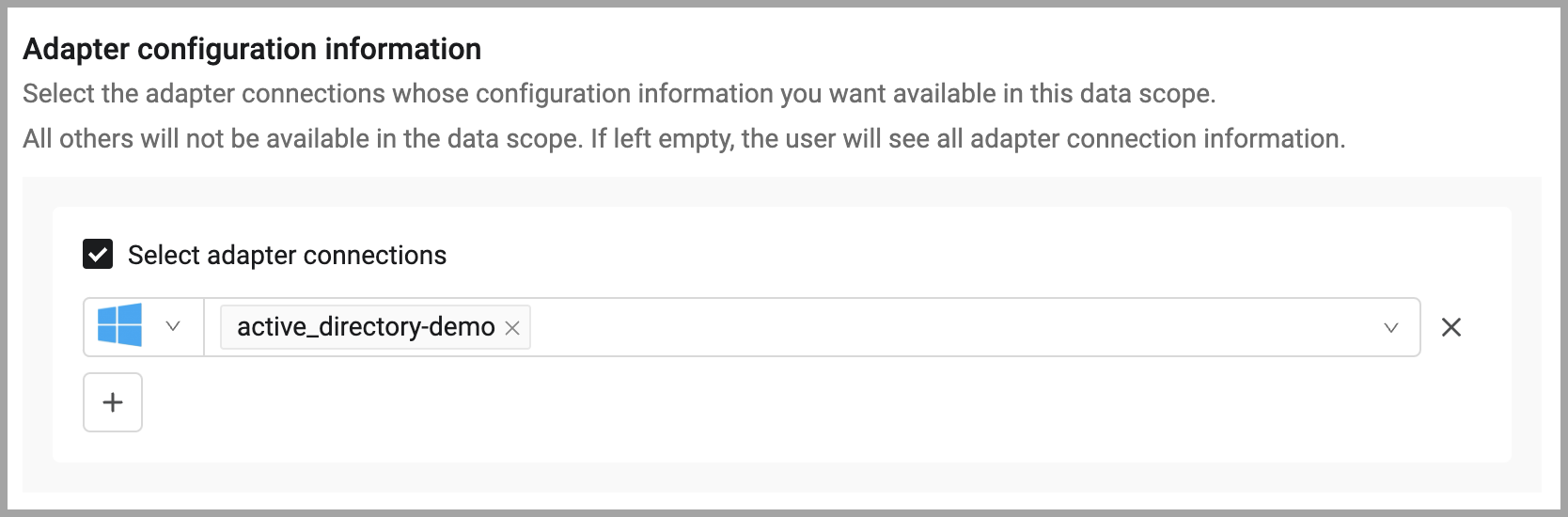
To hide or reveal adapter connection information:
- On the Restrictions tab, in the Adapter configuration information section, choose Select adapter connections.
- Select the adapters and adapter connections whose information you want available in the data scope. All others will not be available in the data scope. If left empty, even if Select adapter connections is selected, the user will see all adapter connection information.
Managing Cloud Accounts in the Data Scope
You can manage which cloud accounts are available to the data scope in the Cloud Compliance Center. When cloud accounts are selected, only the selected accounts are available. When left empty, all cloud accounts are available.
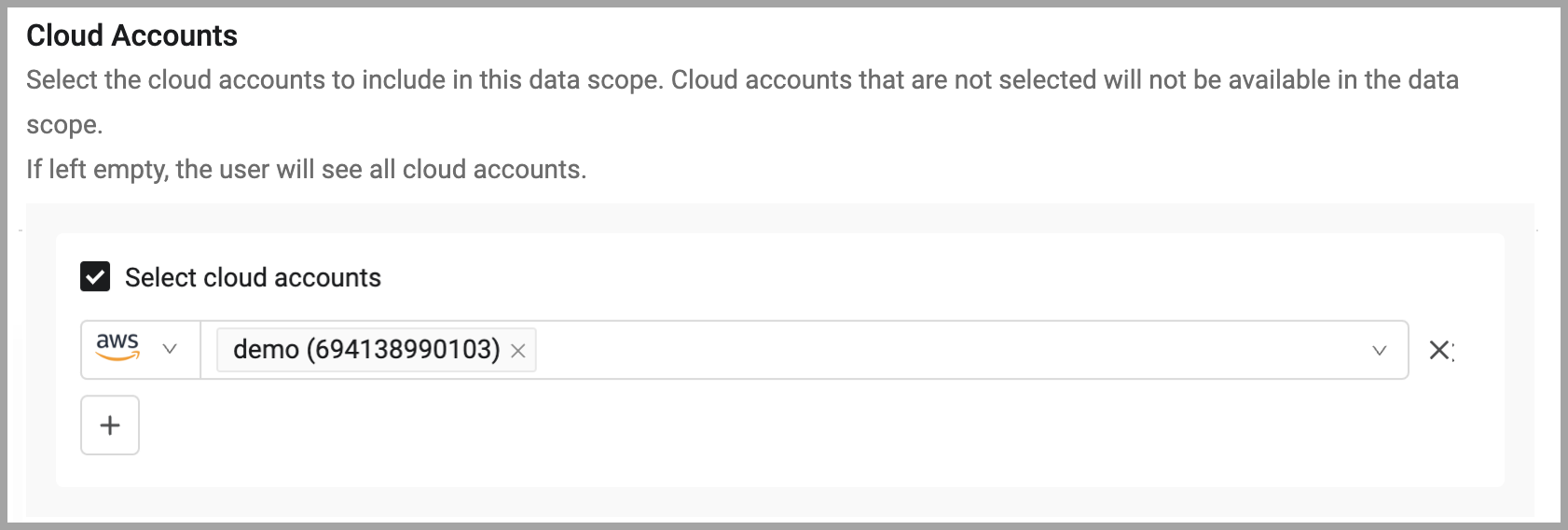
To select cloud accounts:
- On the Restrictions tab, in the Cloud accounts section, choose Select cloud accounts.
- Select the adapters and cloud accounts you want available in the Cloud Compliance Center for this data scope. All others will not be available in the data scope. If left empty, even if Select cloud accounts is selected, the user will see all cloud accounts in the Cloud Compliance Center.
Creating an Asset Scope Query
An asset scope query can be used to define the assets included in a data scope. The assets returned by the query are included in the data scope. For example, they can be determined by installed OS, IP addresses, or tagged assets or any other queryable data.
Note
Existing saved queries cannot be used as data scope queries.
Data Scope queries cannot use other saved queries as part of the data scope definition.
- Use the Query Wizard to create a new query according to the criteria you require.
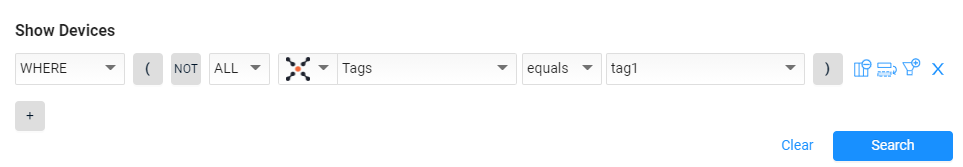
-
Click Search, all relevant assets are displayed.
-
Click Save As to save this query.
-
The Save As New Query dialog opens.
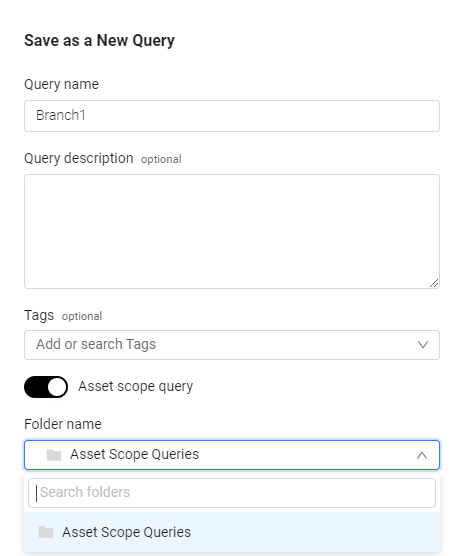
- Enable Asset scope query to save this query as an asset scope query, select a folder to save the query and click Save. By default asset scope queries are saved in the Asset Scope folder.
Note
The Asset Scope query toggle is only visible for users with relevant permissions.
When you open the Queries page, this query appears in the Asset Scope Query folder. The results of an asset scope query define the set of data included within a data scope and on which a user can perform all Axonius activities.
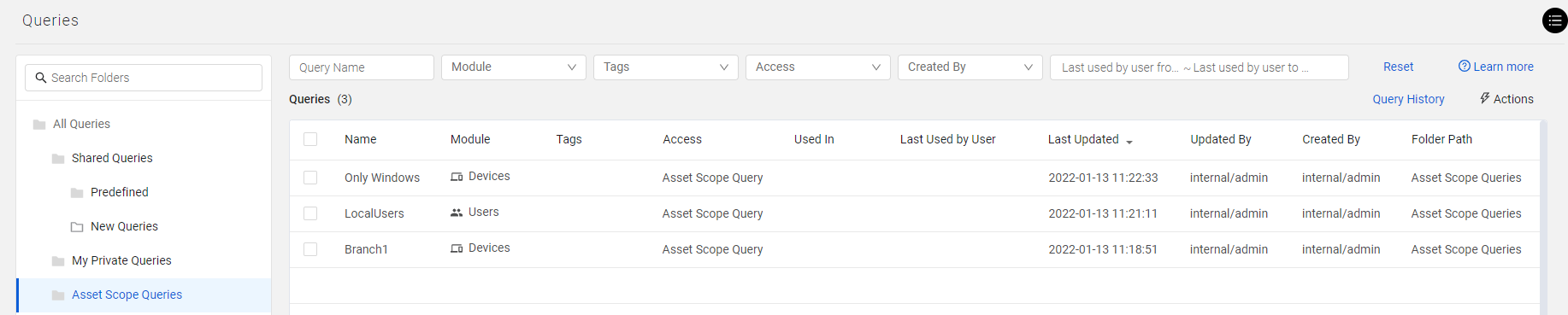
Note
Users who have Manage data scope permissions can use asset scope queries like any other saved query (for instance, when creating dashboard charts, etc.).
Creating an Asset Scope Query from the New Data Scope Drawer
You can also create a new Asset Scope query directly from the New Data Scope drawer. To create a new Asset Scope query
- Click Add Query; the Query Wizard opens.
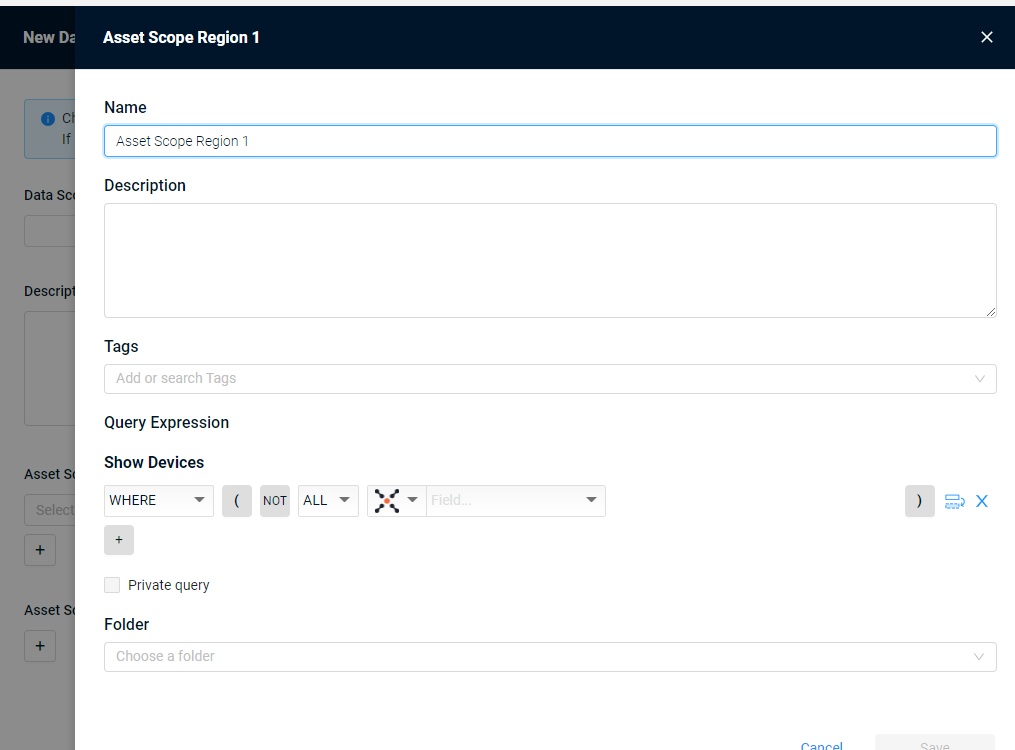
-
In Name, enter a name for the new query.
-
In Description, enter a description that includes what assets the query returns.
-
In Tags, add tags if necessary.
-
In Cache Settings, select whether to Always keep cached or deselect to not keep cached. When selected, query results are updated and stored in cache. This makes the query run faster.
Note
This option only appears when the Enable caching on recently used queries option is enabled in the Cache and Performance settings.
- In Query Expression, select the query parameters. For more about using the Query Wizard, see Creating Queries with the Query Wizard.
- Select a folder to save the query and click Save. By default asset scope queries are saved in the Asset Scope folder.
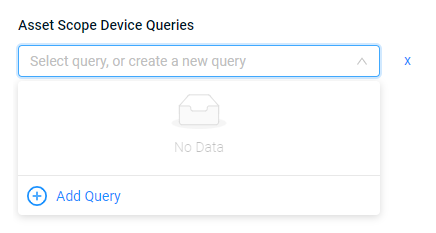
The new query appears as an asset scope query on the Queries page.
The query drawer closes and you are returned to the New Data Scope drawer.
- Click Save, the new Data Scope you created appears in the Data Scope list.
You can edit/delete the data scope as required.
Note
If you do not choose any asset scope queries at all, then the assigned users will have access to all assets on the system.
Duplicating a Data Scope
You can duplicate a data scope to create a new data scope with small changes from an existing one To duplicate a data scope
-
Select a data scope on the Data Scope Page. The Data Scope drawer opens.
-
Click the duplicate icon; a duplicate of the data scope is created named Copy <data scope name>.
-
Rename the data scope and edit as required, then select Save.
Updating the Data in a Data Scope
From the Add Data Scope menu, click Edit Data Scope Settings to define the frequency at which the data scope data is updated. These settings apply to all data scopes.
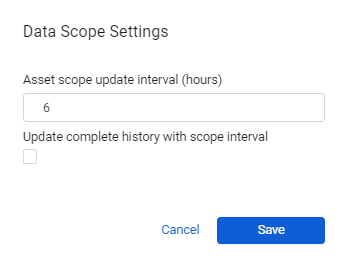
- Set the frequency in hours in which the asset scope query results are updated. The default value is every 6 hours.
- Select Update complete history with scope interval to include historical data in the asset scope, otherwise the relevant roles can see data only from the day the scope was created.
Editing Asset Scope Queries
When you edit an asset scope query, the set of assets available to the users associated with the data scope is updated accordingly.
Note
Be careful when you change an asset scope query. This affects the scope of the assets included in dashboard charts, Reports, Enforcement Actions, etc. that the users assigned to the data scope have created.
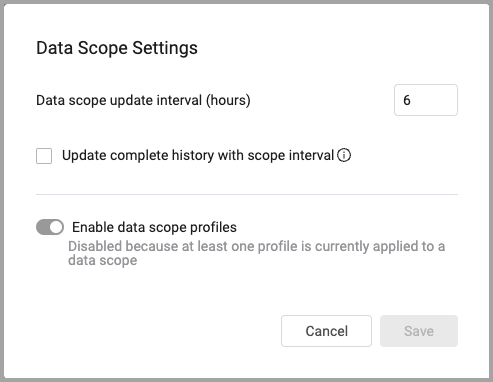
Data Scope Settings
Use data scope settings to configure the following:
- Data scope update interval (hours) - Asset scope queries are updated every X hours.
- Update complete history with scope interval - When selected, and the data scope queries have been updated, historical data is re-filtered according to the new query parameters.
- Enable data scope profiles - When selected, you can apply data scope profiles to data scopes. When data scope profiles are enabled, the "Data scope profile" section is added to the top of the data scope configuration drawer (including existing data scopes).

Note
When a profile is applied to a data scope, profiles cannot be disabled. To disable data scope profiles, first remove all profiles from all data scopes. Then disable them in Data Scope Settings.
To access data scope settings:
-
From the top right corner of any page, click
.png) . The System Settings page opens.
. The System Settings page opens. -
In the Categories/Subcategories pane of the System Settings page, expand User and Role Management, and select Data Scopes.
-
The Data Scopes tab is displayed. Data scope settings are only accessible from the Data Scopes tab.
-
Click Settings.
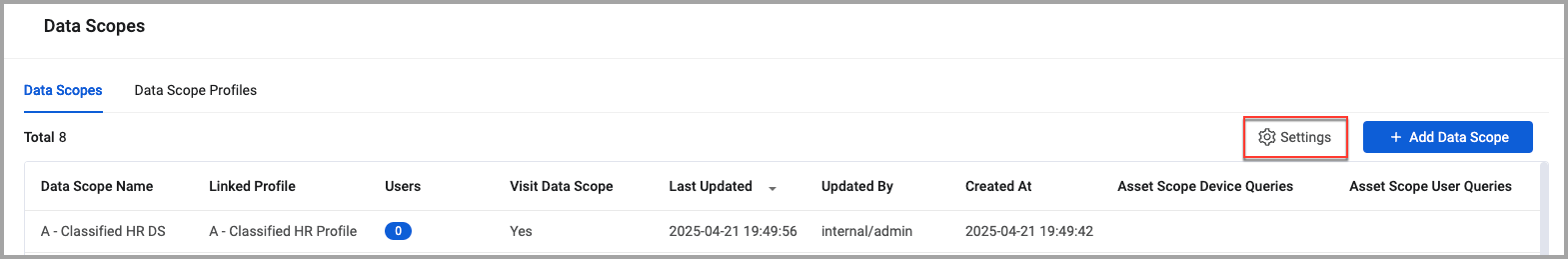
The Data Scope Settings dialog is displayed.
Updated 22 days ago