Creating Enforcement Action Dynamic Value Statements
Overview
Use Dynamic Value statements (also referred to as 'statements') to add dynamic values to fields in Enforcement Actions using values from the assets themselves.
-
The Configure Dynamic Values toggle appears in each Enforcement Action, which has additional parameters that you can configure. Any user with either Add Enforcement or Edit Enforcement permission, or both, can create statements.
-
Optionally set Dynamic Value statement settings to configure how the Dynamic Values are processed.
-
Two types of statements are available for use:
- "All" statements - These statements read over all the assets in the asset pool one by one and populate the values fetched from the asset itself into Action form fields.
- Switch/Case statements - These statements check an asset field (declared in the switch) for multiple criteria (each declared by a case) and use those values to populate the Action fields.
-
Dynamic Value statements support asset, Activity Logs, and Adapters Fetch History modules. They do not support Asset Investigation and Findings modules.
-
An Enforcement Set, which is configured with a Dynamic Value statement, runs only on query results filtered according to the data refinement configuration. This is the case for queries filtered with any data refinement option, except 'Refine field values by adapter connection'.
-
Furthermore, the Dynamic Value statement automatically ignores field values filtered out of asset list fields as a result of data refinement, i.e., empty (null) list field values. For example, if the Axonius - Add Custom Data to Assets enforcement action runs on a query that has been refined to only include low CVE severities, and is configured with a Dynamic Value statement that counts CVE severities. In this case, the count function counts only the number of low CVE severities, and does not count the medium and high CVE severities, which have been replaced in the list field by empty (null) values following data refinement. Example: A Device asset contains the Host Name list field [gcp-dbnginx1, Fallback, gcp-dbnginx2]. An Enforcement Set is configured to run an Enforcement Action on a query in which Host Name is filtered using Refine Data to remove Host Name 'Fallback'. The above Host Name is returned from the query filtered with data refinement as [gcp-dbnginx1, null, gcp-dbnginx2]. The Dynamic Value statement with the count function (see below) returns 2 (# of host names) and not 3, as it ignores null values.
device all then form.field_integer set_value count ([device.specific_data.data.hostname])Note
An Enforcement Set that is not configured with a Dynamic Value statement runs on all assets, as data refinement does not remove assets from the query.
-
Some examples for the use of statements:
- You can create an Enforcement Set with its main action to create a ticket/incident. In the statement, you can determine how to fill the description or summary fields of the ticket/incident with information from the asset.
- You can create an Enforcement Set with its main action to Add Tag to Assets. In the statement, you can set criteria to assign different tag values to different assets.
- You can create an Enforcement Set with its main action to Add Custom Data to Assets. In the statement, you can create a calculated custom field based on values from several fields, create a custom field to assign a numerical rank to vulnerabilities, and much more.
Dynamic Value Statement Settings
Dynamic Value Statement settings control how the system handles empty asset field values and dynamic value failures are handled. Enabling Configure Dynamic Values reveals a Settings icon (see below). An orange dot on this icon indicates that at least one setting is enabled.
Clicking the icon displays the following options:
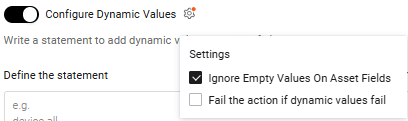
Ignore empty values on asset fields
The Ignore Empty Values On Asset Fields option (enabled by default) ensures the Dynamic Value Statement ignores empty (null) values in multi-value asset fields and operates only on non-empty values. This prevents empty values in a list field from causing Dynamic Value processing failures.
If this option is disabled, the statement processes all values in a multi-value field. If any value is empty, the entire statement fails, and the configured fallback value is used.
Example: concat ([field1("aaa")], [field2(null)], [field3("ccc")]) results in ["aaa","ccc"] when this option is enabled, but fails (resulting in the fallback value) when disabled.
Note
This option only applies to multi-value fields. An empty value in a single-value field always causes the function to fail.
Fail the action if dynamic values fail
The Fail the action if dynamic values fail option, disabled by default, controls how Enforcement Actions behave when a dynamic value fails to meet the Dynamic Value Statement criteria.
-
When enabled, if an asset's dynamic value doesn't meet the defined criteria, the Enforcement Action is halted and logged as 'Failed.' The following error is also logged: "Dynamic value processing error - Action failed. Details: [Error Code/Message]". This is useful in scenarios like "Create User" actions, where using an irrelevant or invalid fallback value is undesirable. Stopping the action entirely is the preferred behavior in these cases.
-
When disabled, the configured fallback value is used, and the action is logged as 'Success,' even if the fallback value is inappropriate.
Creating the Statement
To create a statement
-
Configure the Enforcement Action. In the Select Action tab, select a Main Action to add to the Enforcement Set. The relevant Enforcement Action dialog is displayed, with a tab for Required Fields and one or more tabs for additional fields. Make sure to fill in all of the required fields with values. These values are used for each relevant field if the Dynamic Value statement gives an empty result as a result of the enforcement set run. For example, when you create an Enforcement Set with Main Action -Add Custom Data to Assets, fill in the Field name and Field value action fields.
-
Toggle on Configure Dynamic Values.
- In the Syntax tab, you can drag the handle at the lower-right corner to resize the Define the statement text box.
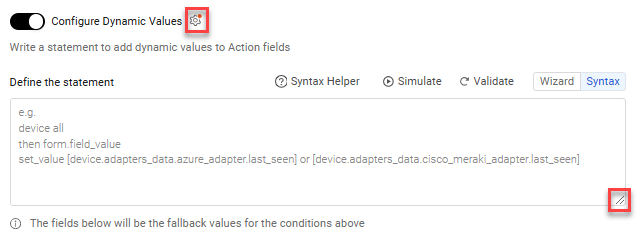
- In the Syntax tab, you can drag the handle at the lower-right corner to resize the Define the statement text box.
-
Optionally, configure the Dynamic Value statement settings.
- Click the Settings icon near the Configure Dynamic Values toggle (see above).
- In the Settings that opens, enable or disable the following options, as required:
-
Determine the type of statement to use:
-
Construct a statement in the Define the statement text box including action form fields, adapter fields, functions, and operators, using either of the following methods:
- The Dynamic Value Statement Wizard.
- If the Enforcement Action includes a custom message (for example, Axonius -Send Email), you can compose the message text using the HTML or Plain Text editor within the Dynamic Value statement. Learn how to use the HTML and Plain Text editors.
- The Syntax Helper with Autocomplete feature
- Click Validate. Axonius checks that the statement syntax is correct. It does not validate field types or values.
- If the syntax is correct, the message 'Statement was validated successfully' is displayed in green under the text box.
- If there is a syntax error, a detailed error message is displayed in red under the text box. Fix the error, and repeat this step.
- Click Validate. Axonius checks that the statement syntax is correct. It does not validate field types or values.
- The Dynamic Value Statement Wizard.
-
Use the Dynamic Value Statement Simulator to debug the statement component by component, until the results meet your requirements.
-
When the Enforcement Set is run, the statement is used.
Syntax Tips
- Static string values must be written within quotation marks " ". For example: "@gmail.com". They should not be pasted from other systems.
- Make sure that the quotation marks are straight and not curly, as curly ones are not supported.
- Functions and operators must be followed by (values) in parentheses.
- A field name following "switch" does not require square brackets.
Note
Dynamic Value statements may "split" the Action into multiple Actions, one for each value configured in the statement.
For example, if 100 assets share the same value configured in the statement, those assets are combined into one run. On the other hand, if the 100 assets all have different values, the Enforcement Set is run 100 times.
More values with matches results in more time for the run to complete.
Examples
Example 1
This example shows how you can create a Dynamic Value statement for the Axonius - Send Email enforcement action, configured configured on Devices matching the Zoom Installed query, with the help of the Dynamic Value Statement Wizard or Syntax Helper.

The first screen below shows how you can use the Wizard to choose an asset field from Devices for the Dynamic Value statement, and the second screen shows how you can use the Syntax Helper.
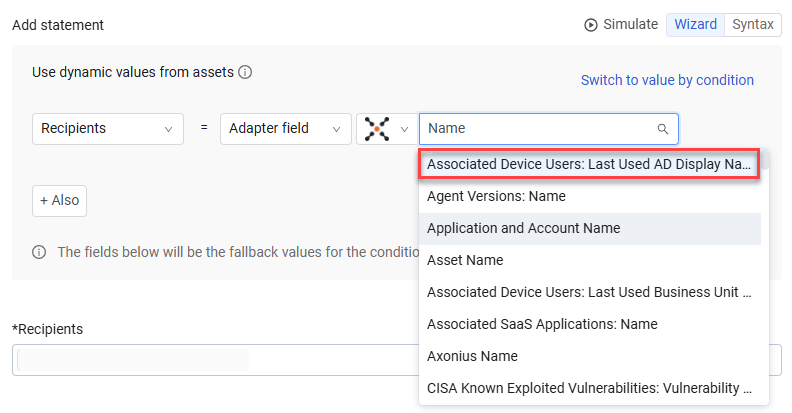
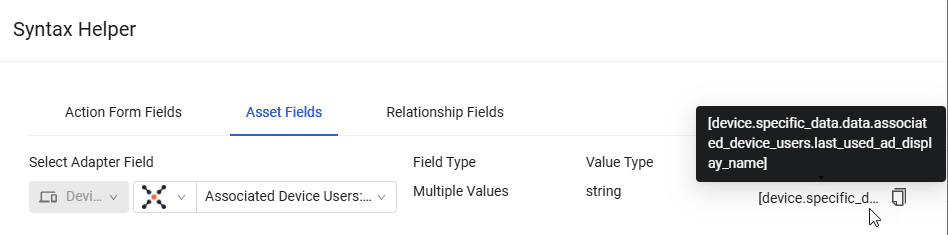
Example 2
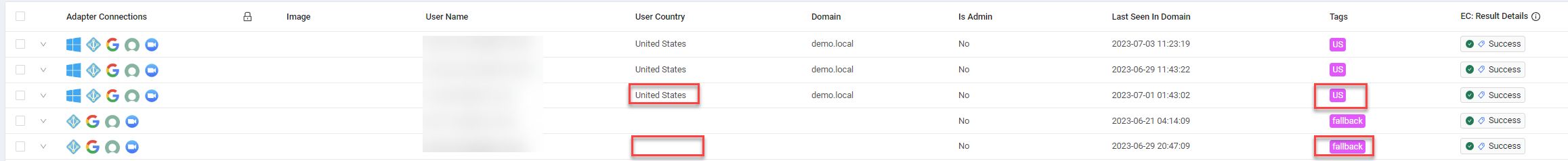
Enforcement Action used:Axonius - Add Tag to Assets In the following Dynamic Value statement used to tag users, all users with their user country field (user.specific_data.data.user_country) having the value 'United States' are tagged with a 'US' tag. Users with no entry for their user country or a country other than 'United States' are tagged with the Tag default value configured in Tag names (in the Enforcement Action configuration dialog) - in this case, "fallback".
switch user.specific_data.data.user_country
case field_equal ("United States") then form.tag_name set_value "US"
Note
It is advisable to give a meaningful default Tag name, such as Fallback, so that it isn't mistaken for a Tag name that is based on an asset field value.
Updated 1 day ago
