Linux SSH
Linux Secure Shell (SSH) uses remote command execution over the SSH protocol to gather information about the endpoint Linux machine, including:
- Hostname
- Network Interfaces - including MAC addresses, IP addresses and subnets
- Operating system, kernel version and distribution
- List of installed software
- Users and admin users
- Hard drives and file systems
- CPUs and RAM
- Services
- Listening ports
- Hardware details, including serials
- and more...
Most of the information fetched from the Linux SSH adapter is also displayed under the various asset Aggregated data tables.
(192).png)
For more details, see Asset Profile Page.
Note
The Linux SSH adapter is a 'read only' adapter. The adapter only gathers information about the endpoint Linux machine and does not change it.
It is safe to use the adapter to fetch information from production environments.
The Linux adapter uses the following Linux commands:
- cat
- df
- dmidecode
- dpkg
- echo
- entstat
- ifconfig
- ip
- isainfo
- lsb_release
- lslpp
- lssrc
- md5sum - If you provide MD5 file list in the Linux SSH adapter advanced settings.
- netstat
- oslevel
- prtconf
- pkginfo
- prtdiag
- pagesize
- rpm
- systemctl list-units
- service
- ss
- svcs
- sudo - If Sudoer option is selected. For details, see below.
- svmon
- uname
- vmstat
The Linux SSH adapter reads the following files from the endpoint:
- /etc/redhat-release
- /proc/meminfo
- /etc/passwd
- /etc/release
- Each file from the MD5 file list provided in the Linux SSH adapter advanced settings. The list must include file path, separated by comma (',')
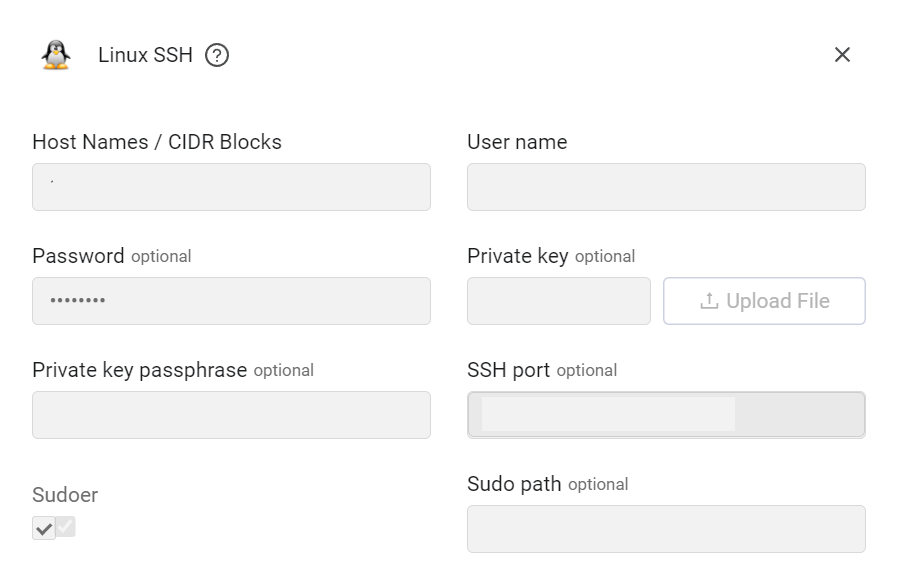
Adapter Parameters
-
Host Names/CIDR Blocks (required) - Enter a comma separated list of DNS Addresses or IP Addresses of the Linux machine, or one or more comma separated CIDR blocks (a CIDR block is in the format of IPv4 address, a slash ('/') character, and a decimal number for example
'192.168.2.0/24would mean all addresses between192.168.2.1and192.168.2.254 -
User Name (required) - The SSH user name to connect with.
-
Password (optional, default: empty) - A password for the SSH user.
- If supplied, the password is used for authentication.
- If not supplied, Axonius will not use the Password for authentication. In addition:
- If you choose the Sudoer option and user password is required to execute privileged commands - the specified password is used to execute sudo command.
- If you choose the Sudoer option and no user password is required to execute privileged commands - leave blank.
NOTE
For authentication, you must specify at least password or private key, but you can also specify both.
- Private Key (optional) - A private key for the SSH user.
- If supplied, the private key is used for authentication.
- If not supplied, Axonius will not use the Private Key for authentication.
NOTE
For authentication, you must specify at least password or private key, but you can also specify both.
- Private Key Passphrase (optional, default: empty) - Specify a private key passphrase if the private key is protected by a passphrase.
- SSH Port (optional, default: 22) - The SSH port.
- If supplied, Axonius will use the specified port for connection.
- If not specified, port 22 is used.
- Sudoer (required, default: True) - Select this if the user is listed as a sudoer and can execute privileged commands (by using the sudo command).
Hardware information such as serials, CPUs and bios versions are fetched only when the specified user can run dmidecode command.
- If enabled, this adapter connection will try to run sudo dmidecode command. The user password will be used, if required.
- If disabled, this adapter connection will usually fail to run that command (unless the specified user is the superuser). Therefore, the hardware information will not be fetched.
- Sudo Path - Specify an absolute path (/path/to/sudo) of a binary to use for sudo'ing to the root user.
- If supplied, when the command line is executed it will be prefixed with the value supplied
- If not supplied, when the command line is executed it will be prefixed with "sudo".
- Verify Fingerprint - Enter a fingerprint. If entered then ssh connections verify that this fingerprint matches the fingerprint of the host's public key. The value can be usually found in ~/.ssh/known_hosts. If missing then no confirmation is done upon connection attempts.
To learn more about common adapter connection parameters and buttons, see Adding a New Adapter Connection.
NOTE
The adapter configuration and logic are also used in the Run Linux SSH Scan enforcement action.
Advanced Settings
Note
Advanced settings can either apply for all connections for this adapter, or you can set different advanced settings and/or different scheduling for a specific connection, refer to Advanced Configuration for Adapters.
- MD5 Files List - Enter a list of full path of files that will have their md5 calculated and added to the device information. The list must include file path, separated by comma (','))
- Network Timeout (default 30) - Set the timeout in seconds for the SSH connection.
- SSH Scan Pool Size (default 40) - Enter a number of hosts to scan in parallel
- Number of hosts to fetch in parallel (default 200)- Enter a number of hosts to fetch in parallel
Note
To learn more about Adapter Configuration tab advanced settings, see Adapter Advanced Settings.
Updated 5 months ago
